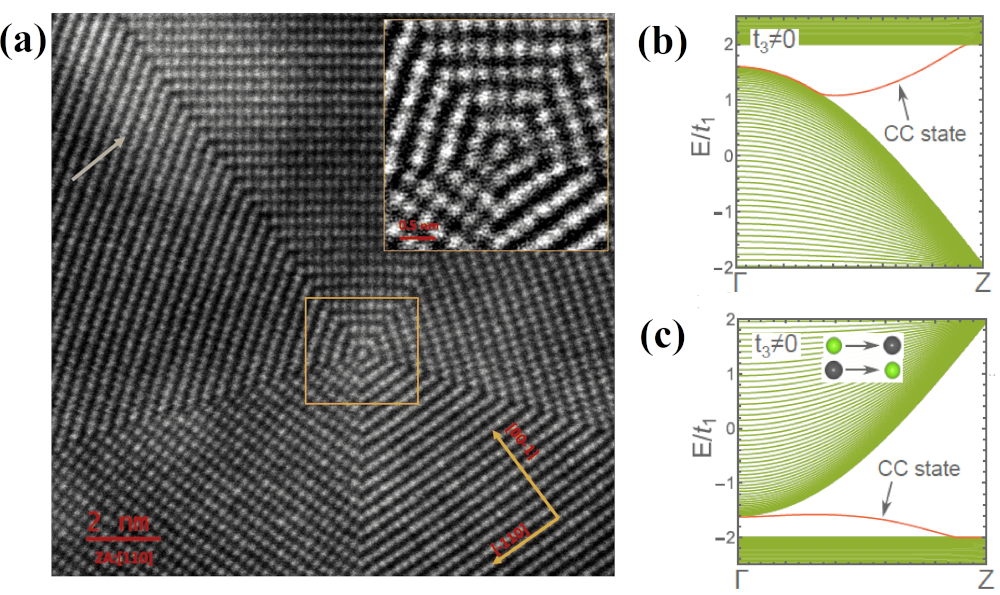
We report on the first experimental realization of pentagonal nanowires within ionic compounds using Pb1-xSnxTe. The disclination and twin boundaries cause the states originating from the core region to generate a conducting band connecting the valence and conduction bands forcing a metallic phase.
This latest publication fo the Institute of Physics presents the experimental realization and theoretical study of Pb1-xSnxTe pentagonal nanowires (NWs). To our knowledge, this is the first pentagonal nanowire based on an ionic compound. The advance is significant, since it is not straightforward to accommodate positive and negative charges on a polygonal shape with an odd number of sides. The structural properties between the core and the shell of the nanowire differ despite the chemical elements and composition being the same; therefore, the authors synthesized unique intrinsic core-shell one dimensional nanowires with distinct properties between the core and the shell region. At the center of the nanowire there is a line defect -- the disclination. The disclination and twin boundary cause the electronic states originating from the NW core region to generate a conducting band connecting the valence and conduction bands, creating a symmetry-enforced metallic phase. The authors have also presented a study of the topological properties related to the central chain of pentagonal NWs using a tight-binding model in connection with the Su-Schrieffer-Heeger model including presence of of defects. Finally, the article unveils these pentagonal NWs as potential candidates for higher-order topology.